In the realm of product development and project management, Scrum stands out as an agile methodology that has revolutionized how teams collaborate and execute complex projects. At the heart of Scrum lie foundational values and pillars guiding teams toward increased efficiency and responsiveness. While the Scrum Guide provides a framework, it’s the adherence to these values and pillars that drives agile transformation and project success.
This article delves into the five core values and three pillars foundational to the Scrum methodology. Embracing these principles enables teams to confidently navigate the complex landscape of modern projects, achieving levels of performance once deemed unattainable. Join us as we explore these crucial concepts and uncover how they can transform your approach to agile project management.
Scrum’s edifice is built on three fundamental pillars: transparency, inspection, and adaptation. These pillars are not only essential for the smooth operation of the Scrum methodology but also embody the spirit of agility, enabling teams to adapt and thrive in an ever-changing environment.

Transparency
Transparency forms the bedrock of trust and openness. Within the Scrum context, it demands that all aspects of the work are visible to those responsible for the outcomes. This means processes, work in progress, and challenges are openly shared with the entire team and stakeholders, ensuring everyone has the same level of information, which facilitates communication and decision-making.
Inspection
Inspection, while non-intrusive, should be a regular activity for Scrum teams. It involves a careful review of Scrum artifacts and progress toward Sprint goals to identify variances or potential issues. Inspection is not just about spotting problems; it’s also about celebrating successes and acknowledging progress.
Adaptation
Adaptation follows inspection. If inspection reveals that aspects of the project deviate from acceptable limits, adjustments must be made. Adaptation is seen as the team’s ability to be agile – to respond swiftly and efficiently to changes without being hindered by a rigid plan.
Together, these pillars support every decision, action, and iteration within the Scrum methodology. They ensure teams remain aligned with project goals while providing the flexibility to adjust to changing demands and lessons learned along the way.
The Five Values of Scrum
Beyond the pillars that structure Scrum, there lies a set of fundamental values that breathe life into this framework. The five Scrum values—commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect—are vital for the successful implementation of the Scrum methodology.
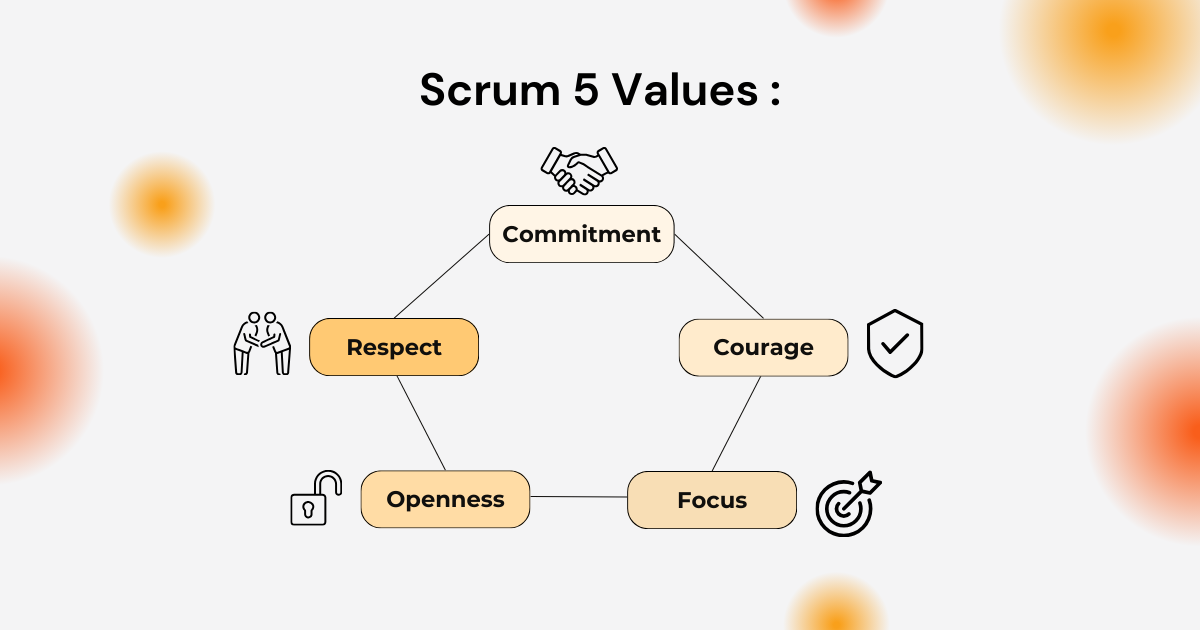
Commitment
In a Scrum team, every member must be committed not only to their individual tasks but also to the team’s goals. Commitment is the collective promise to work towards a common objective and achieve the quality standards set together.
Courage
Courage is essential for a Scrum team to face challenges and make tough decisions. Scrum encourages team members to speak up about issues and advocate for what they believe is the best course of action for the project.
Focus
Focus is the unwavering concentration on the most crucial goals and tasks at any given time. In Scrum, this focus helps teams direct all their energy toward achieving Sprint objectives, undistracted by peripheral matters.
Openness
Openness in Scrum means being transparent about work progress and receptive to feedback. It also involves being open to exploring new possibilities and accepting change based on feedback and inspection results.
Respect
Mutual respect is indispensable within Scrum teams, where members value and support each other’s contributions. This creates an environment where continuous learning and knowledge sharing are encouraged, and everyone is respected for their skills and experience.
These 5 Scrum values are not optional add-ons to Scrum; they are an integral part of it. When teams embody these values, they reinforce the Scrum pillars and create an environment where agility can truly flourish.
Integrating Scrum Values and Pillars into Core Practices
For the Scrum values and pillars to be effective, they must be embodied in all aspects of the methodology, including roles and ceremonies. While roles like the Scrum Master and Product Owner, as well as events like Sprints and Daily Meetings, are topics we’ve already explored in depth, their connection to Scrum’s values and pillars deserves emphasis.

Scrum Values through Roles
The Scrum Master is often seen as the guardian of Scrum values, facilitating commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect within the team.
The Product Owner embodies these values by clearly defining the vision and ensuring the team remains focused on priority objectives. Every team member, by fully engaging in their role, demonstrates these values in their daily work.
Scrum Pillars at the Heart of Scrum Events
Scrum events, such as Sprint planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint review, and Sprint retrospective, are opportunities to practice the pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
For example, Daily Scrum enhance transparency by updating the team on progress and obstacles. Sprint Retrospectives are a key moment for inspection and adaptation, allowing the team to reflect on the past Sprint and adjust for the next.
By integrating Scrum’s values and pillars into roles and ceremonies, teams can realize the full potential of this methodology. It’s this integration that enables true and lasting agile transformation within teams and organizations.
Key Concepts from the Scrum Guide: Essential Principles and Practices
Exploring the Scrum Guide reveals a set of key concepts which, although not explicitly named as principles, are essential foundations of agile methodology and agile project management.

Transparent Collaboration and Communication
At the heart of the Scrum framework is intense collaboration and transparent communication. This extends beyond mere team member interaction, encompassing ongoing dialogue with clients and other stakeholders. Such openness ensures alignment and mutual understanding, which are critical for agile project management.
Self-Organization and Collaborative Decision-Making
Self-organization is a concept that drives Scrum’s effectiveness. By entrusting teams with the responsibility to manage their work and decision-making processes, the framework promotes a culture of accountability and commitment. This autonomy not only facilitates better handling of unexpected events but also optimizes work by aligning team objectives with client expectations. Decision-making thus becomes a collective responsibility, enhancing commitment to the project and operational efficiency.
Flexibility and Continuous Planning
Flexibility is a defining feature of Scrum, allowing teams to adjust based on lessons learned from each sprint and client feedback.
Continuous planning is a dynamic process, crucial for navigating the complexity and uncertainty of projects. This aspect of Scrum ensures that plans are consistently revised and adapted to best meet the current needs of the project, keeping the team focused on delivering the most relevant value.
Continuous Delivery and Regular Feedback
Continuous delivery of product increments showcases Scrum as a standout agile framework. It fosters the frequent rollout of features that can be tested and evaluated by end-users.
Regular feedback is a powerful tool for product refinement, enabling teams to make targeted adjustments and ensure that each new version adds real and tangible value. For instance, the Sprint Review facilitates the collection of user feedback at the end of each iteration.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is essential in Scrum, empowering teams to enhance their processes and elevate the quality of their work. Through Sprint retrospectives, the team learns, adjusts, and evolves, making adaptation not just a reaction but a proactive strategy.
Technical Excellence
Technical excellence, often overlooked in discussions about Scrum, is crucial for delivering a high-quality product.
Solid development practices, supported by continuous integration, ensure that the product is not only functional but also sustainable and maintainable in the long term. Continuous testing and regular code integration contribute to a development cycle where quality is built in from the start.

Conclusion
In this review article, we’ve traversed various facets of Scrum. From its fundamental values to its structural pillars, we’ve seen how these elements intertwine to form a powerful framework for agile project management. Adhering to these principles is not merely about compliance with a guide but a commitment to a profound transformation of processes and team culture.
Transparency, inspection, and adaptation are not mere concepts but the engines of a work dynamic that enables teams to respond with agility and efficiency to the complex challenges of modern projects. Scrum values—commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect—are the ethical pillars that inspire daily behaviors and decision-making.
Adopting this framework is choosing a path toward continuous improvement, maximized customer value, and excellence in product delivery. It’s a commitment to better understanding and collaboration within teams and with clients, constantly adapting to market changes.
Integrating these values and pillars into your approach lays the groundwork for remarkably responsive and resilient project management, capable of overcoming obstacles and seizing opportunities with agility and confidence. The Scrum methodology is not just a set of rules to follow; it’s a work philosophy that can radically transform how projects are conducted and products are developed, for renewed efficiency and success.
For Further Exploration
- Link to the Scrum Guide: Dive into the official Scrum guide for a thorough understanding of Scrum principles and practices.
- Scrum Ceremonies Cheat Sheet: Read our complete cheat sheets on Scrum ceremonies to master all ceremonies of this Framework.
- The Role of the Scrum Master: Discover the essential role of the Scrum Master in the success of Scrum projects.
- The Role of the Product Owner: Explore the responsibilities of the Product Owner in detail with this comprehensive article.
- Best Sprint Retrospective Templates: Use our Scrum retrospective templates for productive and constructive meetings.